1.52 -1.54 Metallic bonding
More than 75% of the elements in the periodic table are metals. Metals are extremely useful materials with a wide variety of uses. This is due to the fact that they have a range of useful physical properties.
all metals are :
- good conductors of heat and electricity
most metals are:
- shiny when freshly cut
- high melting point solids
- ductile and malleable
many metals are:
- strong
- sonorous
Assumed background knowledge:

1.37 - 1.39 Ionic bonding - transferring charge
1.52C Activity 1. Representing metals
Students should:
- 1.52C know how to represent a metallic lattice by a 2-D diagram
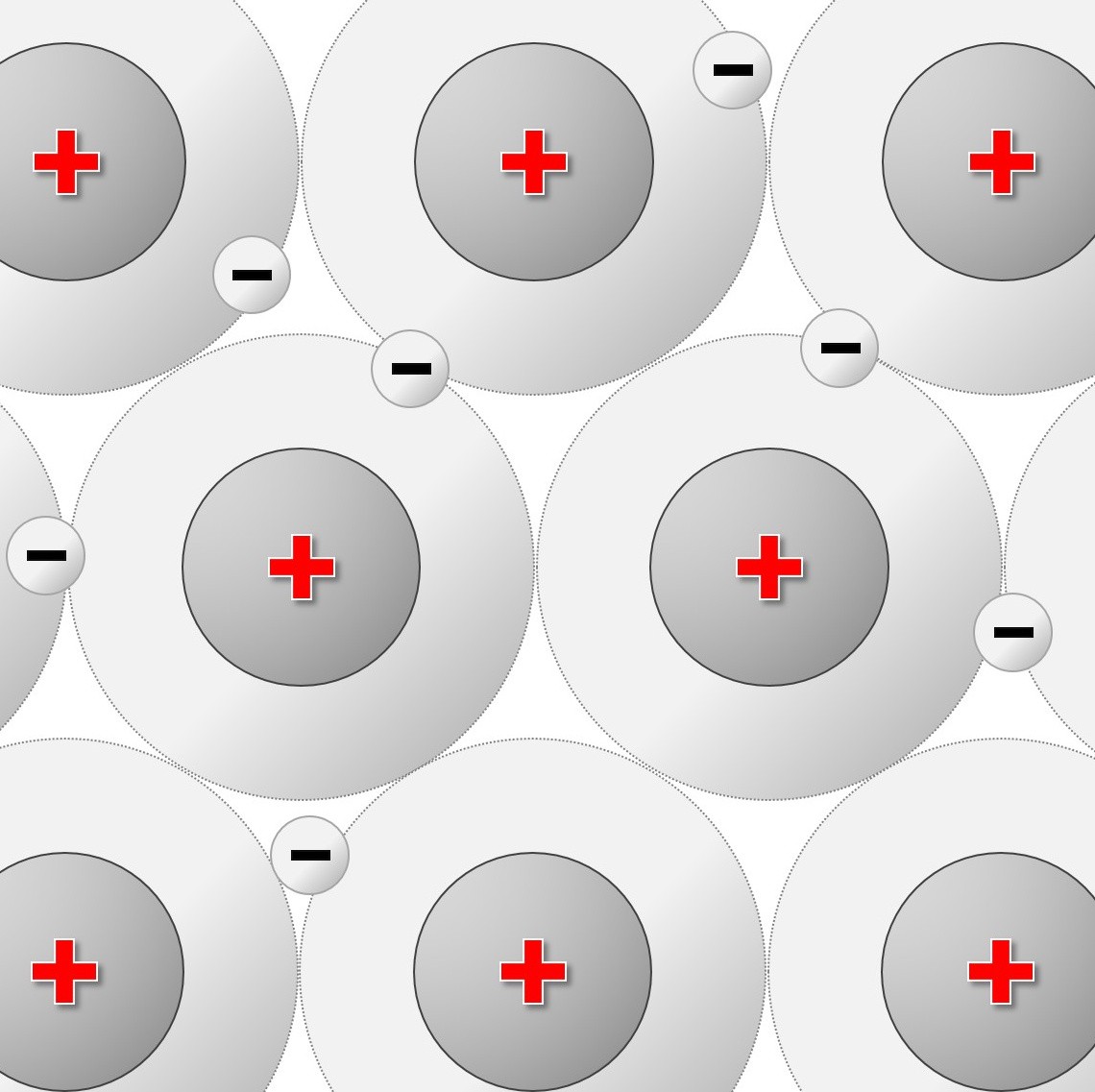
You will have seen in earlier topics how metals tend to form positively charged ions. This happens when the metal atoms lose electrons. In metal atoms the outer shell of electrons is not held strongly to the atom. This means the outermost electrons can move freely throughout the structure.
Since electrons are negatively charged ( and occupying the spaces between the positive ions) the attraction that exists between these opposite charges results in strong bonding within the lattice.
1.53 - 1.54. Activity 2. Metallic bonding
Students should:
- 1.53C understand metallic bonding in terms of electrostatic attractions
- Why are saucepans made of metal?
- Why is the core of electrical cables made of metal?
- What property of metals makes it possible to make them into different shapes?
- What does the term ductile mean?
- How are metal ions arranged in a metal structure
- Why do most metals have high melting points?
- What is metallic bonding?
- Metals are good conductors of heat.
- Metals are good conductors of electricity.
- Metals are malleable because of the layers of atoms.
- The object can be stretched into a wire.
- The ions are arranged in a lattice structure.
- Metals have strong interatomic forces that require a lot of energy to overcome.
- The metal atoms are held together by delocalised free-floating electrons.
1.54 Activity 3. Metallic properties
Students should:
- 1.54C explain typical physical properties of metals, including electrical conductivity and malleability
- What can you say about the number of electrons in the outermost shells of metal atoms?
- How does this explain the conductivity of metals?
- What can you say about the density of most metals?
- Why is is difficult to vapourise most metals?
- Why are most metals shiny?
- Why do metals make a ringing sound when struck?
- Most metal atoms have an outer electron shell that is less than half full.
- As the atoms in a metal are joined by a sea of electrons which can conduct heat and electricity.
- Most metals have a high density.
- Metals have strong intermolecular and interatomic bonds.
- The free electrons can absorb and re-emit light.
- Sound waves can travel between the metal crystals easily.