1.8 Elements compounds and mixtures
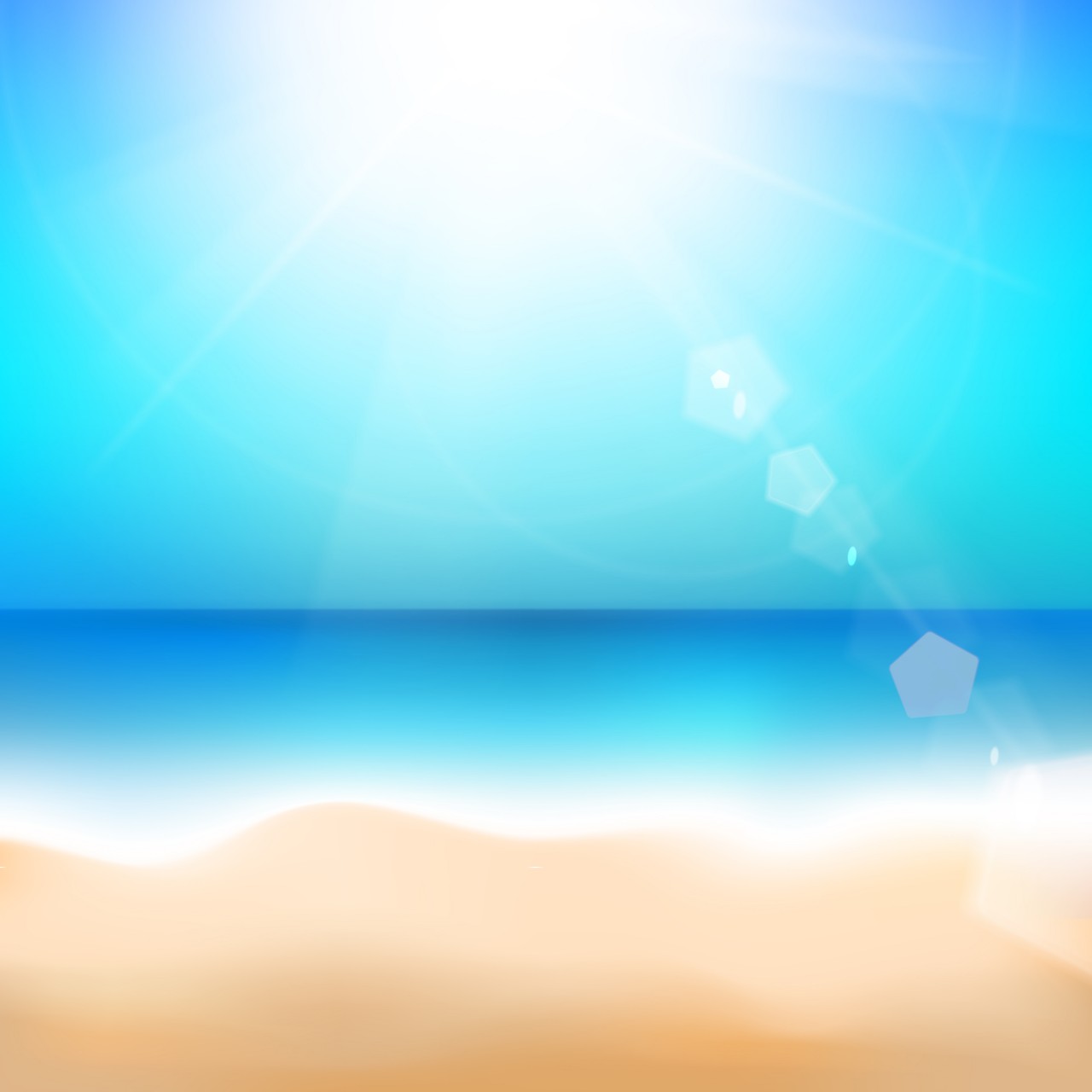
Sun and air?
Study the seaside image for a few seconds . Try to describe it:
You might say that the image shows : A calm sea, clear blue sky, bright sunshine and a perfectly smooth beach.
You could describe it in terms of the states of matter visible:
| SOLID | Sand |
| LIQUID | Sea |
| GAS | Air |
| GAS and PLASMA | Sun |
But as a chemist you might be asked to classify each of these four components as either mixtures, compounds or elements. This section will help you to do that.
1.8 Meet the Elements
Students should:
1.8 understand how to classify a substance as an element, compound or mixture
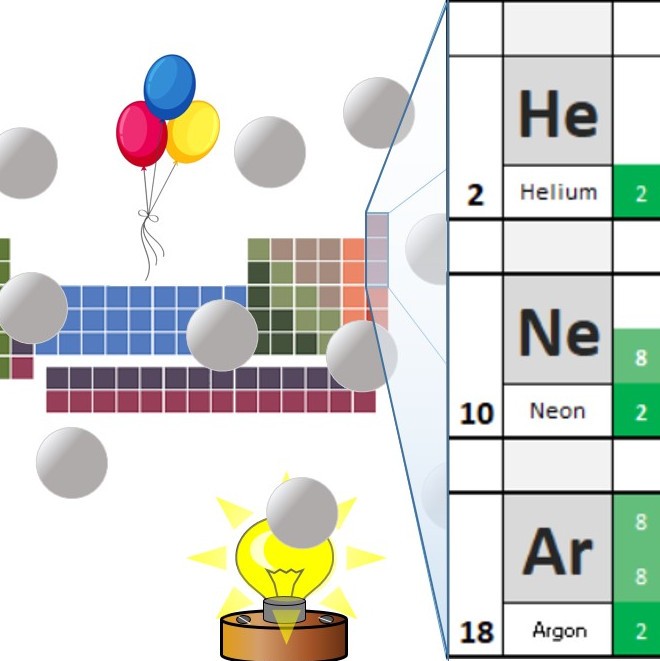
The chemical elements are all listed on the periodic table. The elements are listed in order of atomic number.
All substances are made up of atoms. All of the atoms in a sample of an element have the same atomic number.
The simplest element is hydrogen. This is the first element in the periodic table as it has the atomic number 1. The Sun produces energy as the result of nuclear fusion of hydrogen atoms. This releases vast amounts of energy and produces heavier elements such as helium. As it is so hot - most of the gas in the sun is actually in the form of plasma ( the fourth state of matter).

Periodic Table – Royal Society of Chemistry
1.8 Mixture or compound?
MIXTURE : A mixture is made up of two or more components which although mixed together can be separated by physical means. The components are not chemically combined.
Air is a mixture of gases. The gases in air are the elements Nitrogen (78%), and oxygen Oxygen (21%), the compound carbon dioxide (~ 0.03%) and the noble gases.
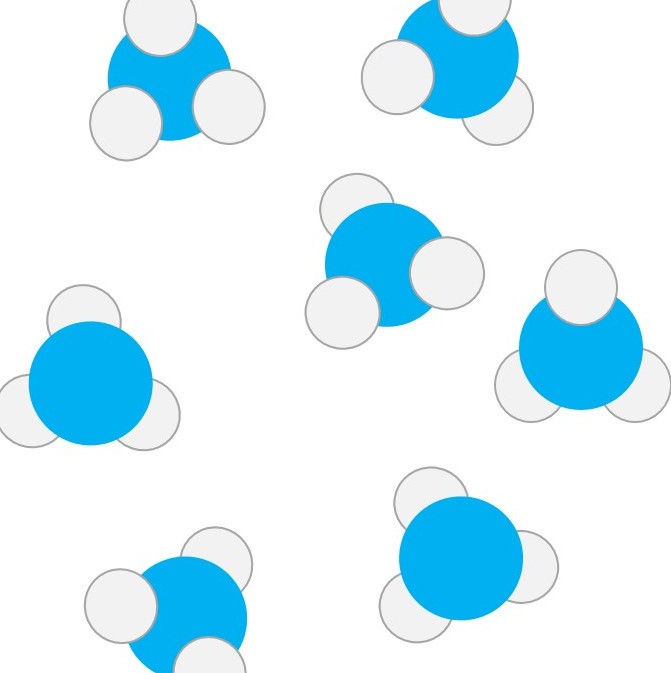
Pure water is a compound with the formula H2O . Seawater contains lots of dissolved salts and lots of minute suspended particles. So seawater is really a mixture too.
COMPOUND : A compound is always made up of two or more different elements in definite proportions joined by chemical bonds. The elements cannot be separated by physical means
Common salt is a compound whose chemical name is sodium chloride. Sodium is a metallic element with the atomic number 11. Chlorine is a non-metal with the atomic number 17.
Sand is made up of tiny particles of rock. The main compound in the rocks which make up sand is silicon dioxide - a compound with the formula SiO2 .
1.8 Some elements up close
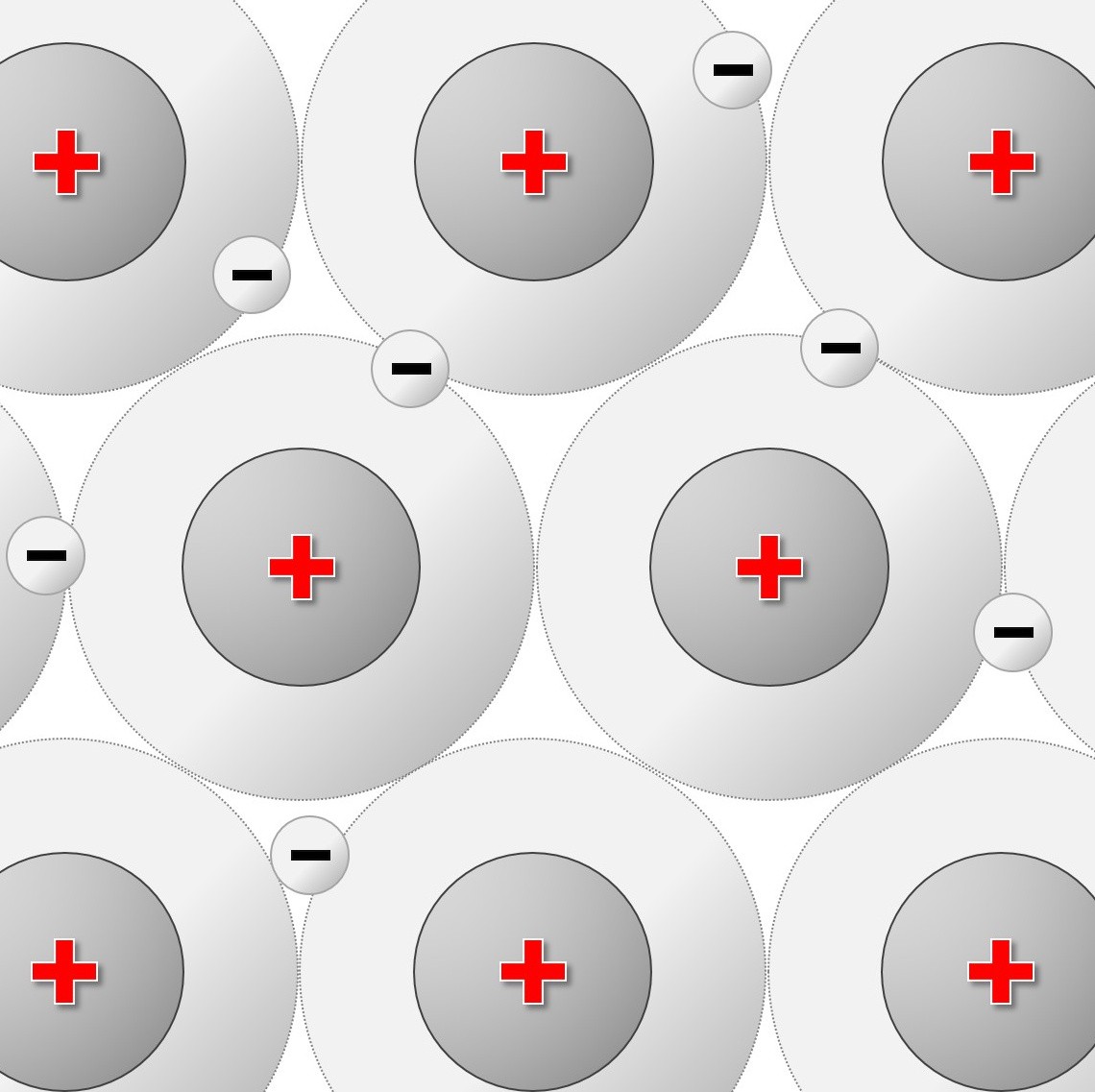
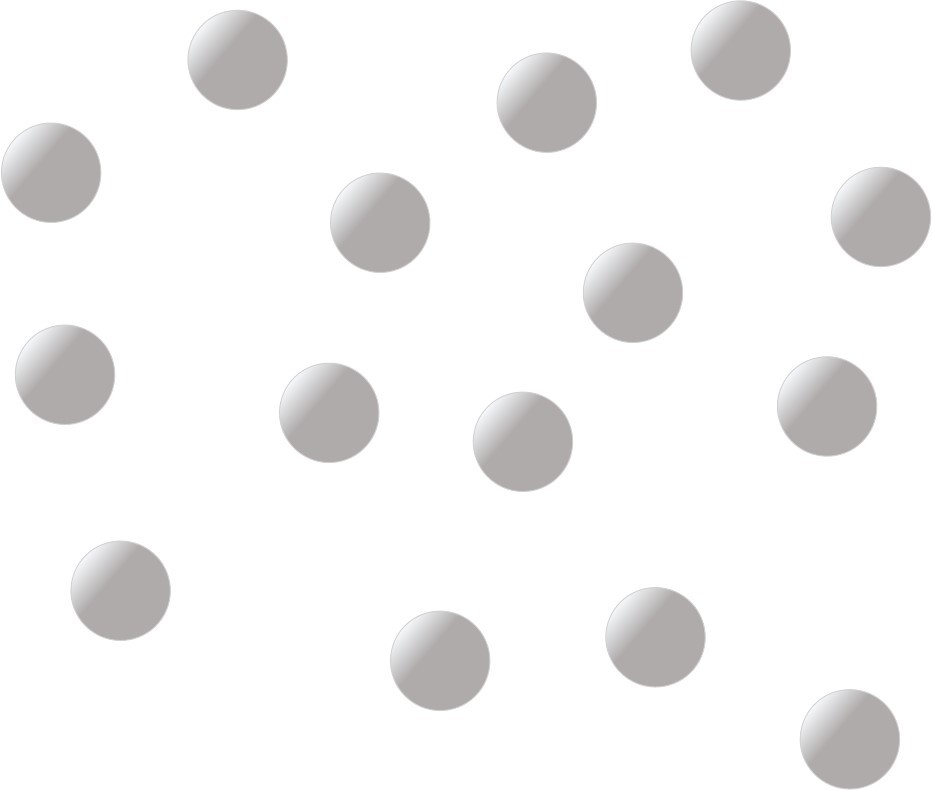
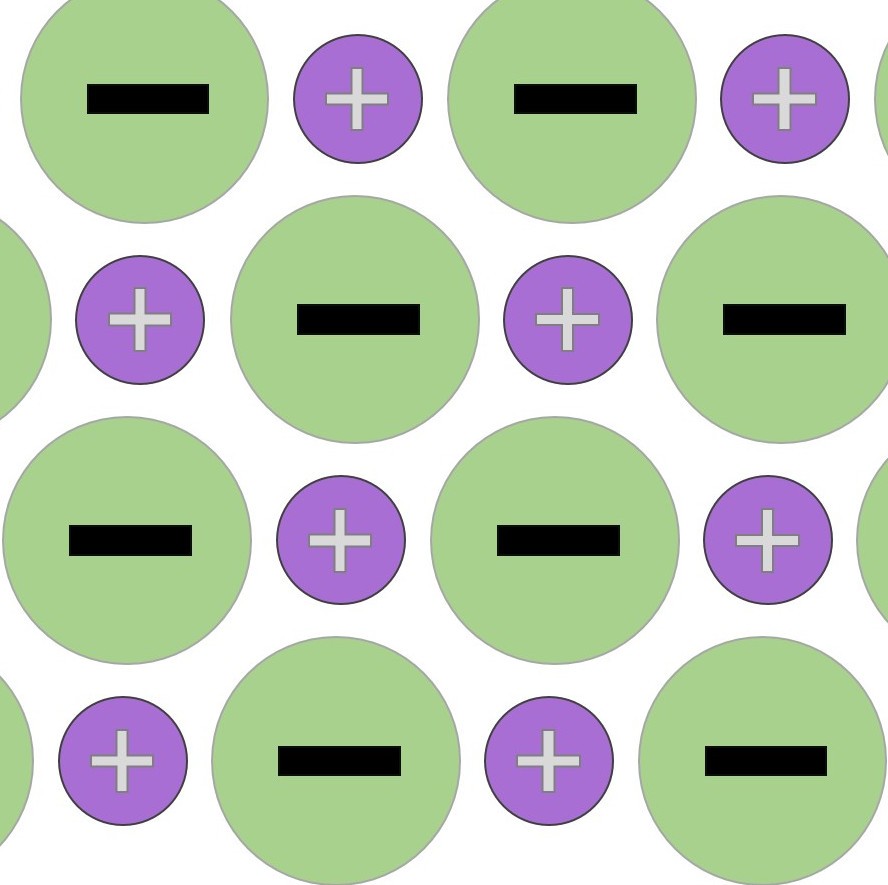
Giant metallic lattices. More than 70% of the elements in the periodic table have a structure similar to this. The negatively charged electrons are "delocalised" and can move from atom to atom.
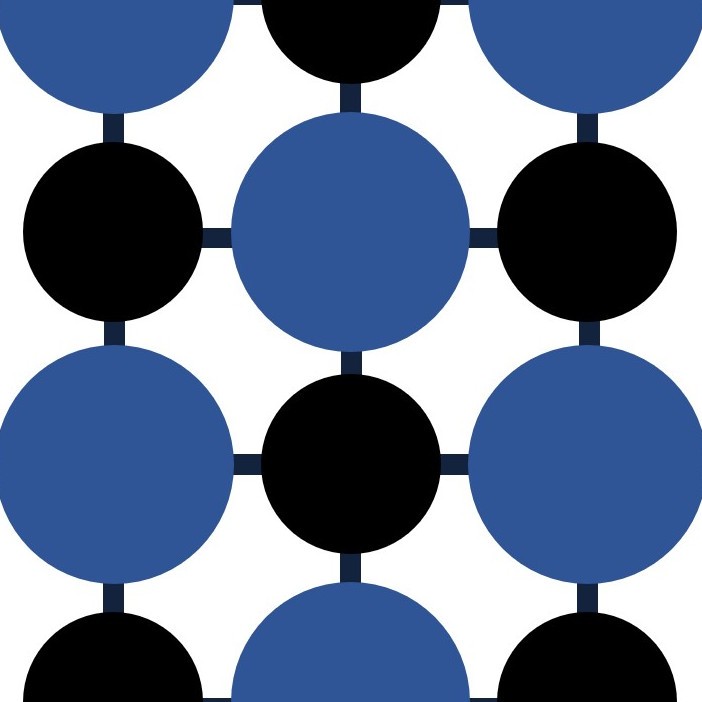
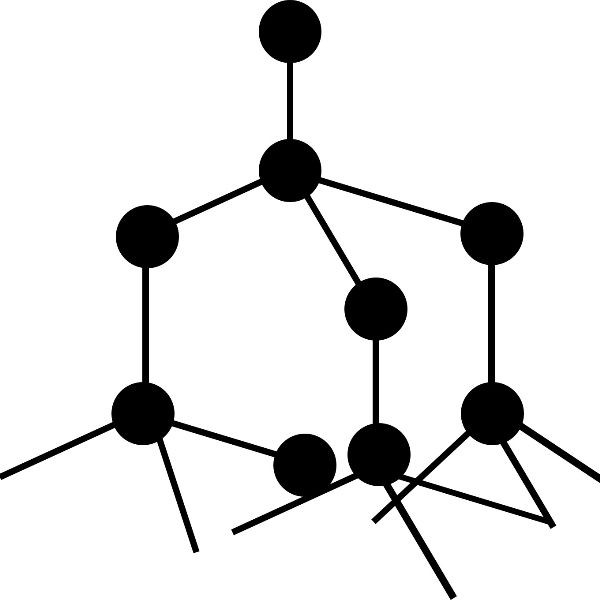
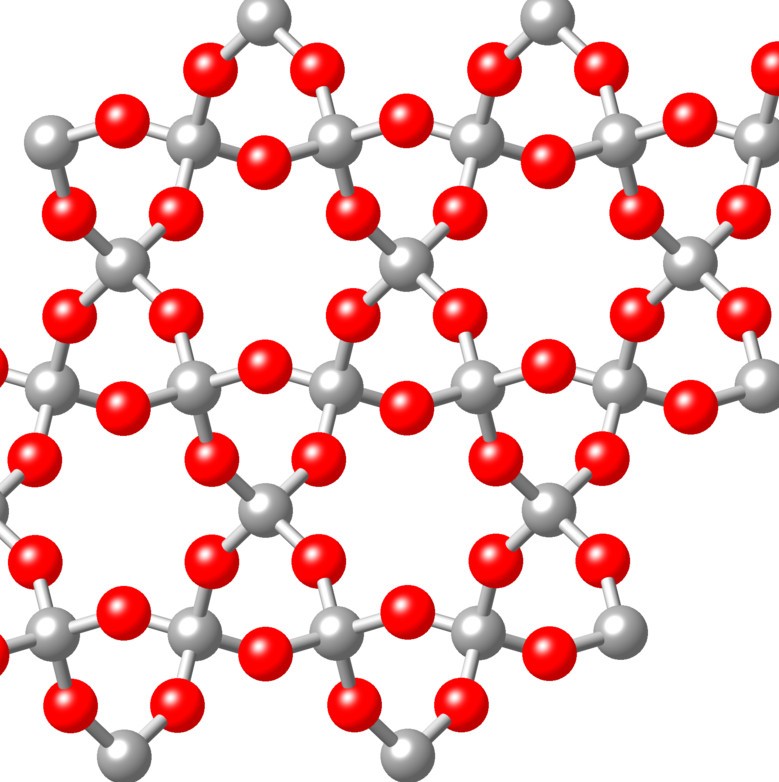
Giant covalent lattices. These elements form giant lattices have high melting points and form crystalline structures.
Diamond and Silicon have structures like this. There are no free electrons in this sort of structure so they do not conduct electricity.
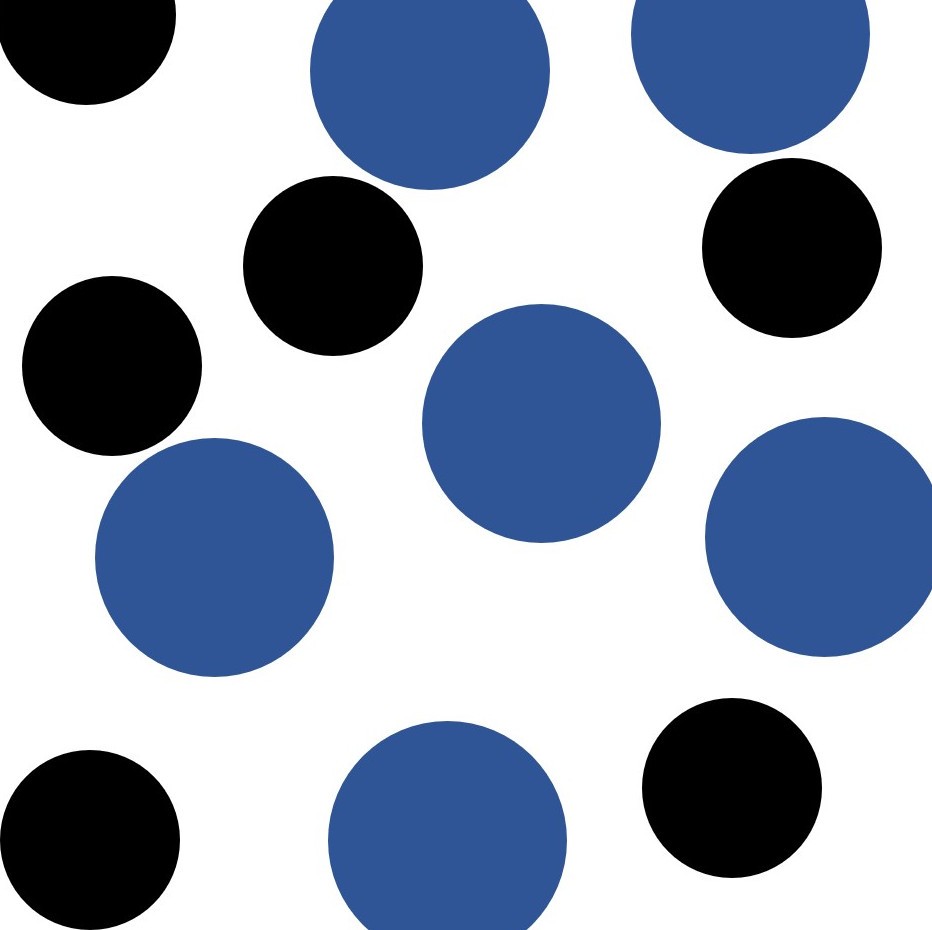
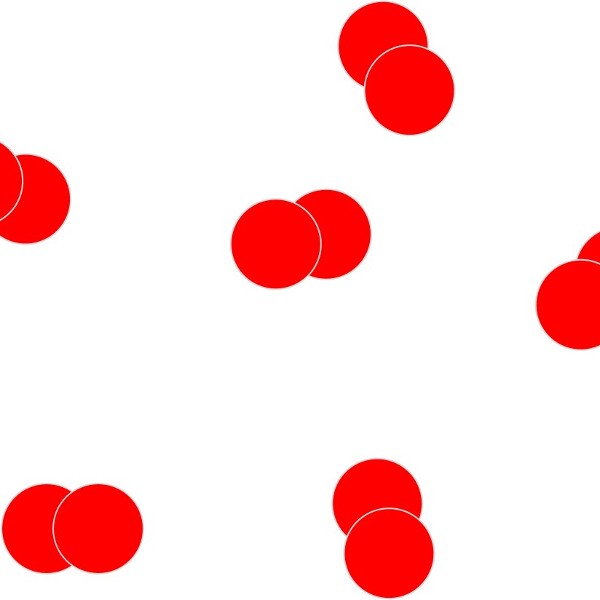
Simple molecular elements. These are often gases at room temperature but can be liquid or easily melted solids.
The atoms shown here are paired up to form diatomic molecules. The forces between the molecules are weak and so elements with this structure will have low melting points and might even be gases at room temperature.
The examples shown here represent:
left: the structure of iodine ( I2) and
right: the strucutre of oxygen (O2)